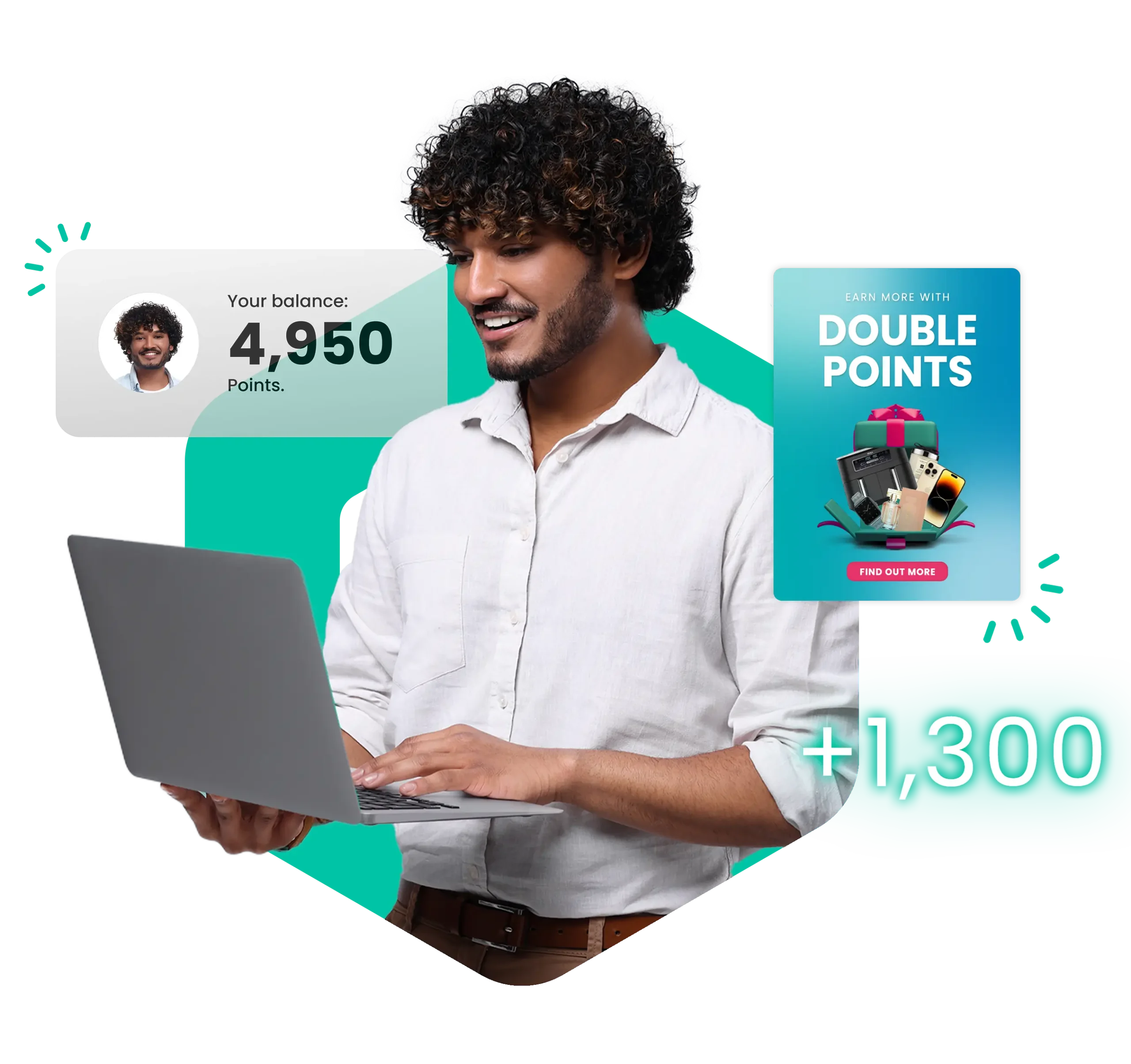
How do you define employee engagement? 🤔
What does attrition rate mean? 😕
What exactly is informal recognition? 🥴
We’ve put together a glossary of employee engagement terms to answer these questions, explain many other terms, help you educate others and improve engagement in your business.
A
Absenteeism: Non-attendance at work without a valid reason. Many of us take time off work due to an emergency or illness, but it becomes an issue when it’s a regular occurrence. By calculating employee absenteeism regularly, businesses can get a good indication of levels of employees satisfaction and engagement.
Absence Management: Absence management is about creating policies and procedures which will reduce employee absenteeism. It’s important for the business to ensure that there aren’t too many employees absent at the same time as this can be disruptive and costly.
Attendance: Measuring employees presence at work, taking into account authorised absences, such as holidays, illness, compassionate leave and un-authorised absences such as voluntary absence without good reason.
Attendance Management: Keeping track of employees working hours using timesheets, spreadsheets or an online attendance platform. This is especially useful for those working on an hourly basis so you can calculate their exact wages. It’s also useful for absence management.
Attrition Rate: The percentage of employees that left your business over a specified period of time. Use this calculator to work out your attrition rate.
B
Benefits: Includes everything on top of the salary as part of an employee’s entitled remuneration, such as pensions, medical or life insurance, discount schemes, childcare vouchers, Bike2Work, counselling and personal development.
Blog: An online website page written in an informal or conversational style. It can be intended for a variety of audiences for any number of reasons, such as entertainment, education, promotion or general sharing of news, views and opinions. (A bit like what you’re reading now!)
Bonus: Usually cash-based rewards that are paid out upon achievement of hitting goals or excellent performance.
C
Channel: The method in which communication is delivered. This could be via email, employee newsletter or social media. (A channel also refers to how you get your products out of the door, such as online or via a third party.)
Collaboration: When employees come together as a team and work to achieve a common goal.
Company Culture: Represents the collective values, beliefs and principles of an organisation. The overall company vision, purpose, mission, leadership style, ethics, expectations and values. It affects the way people interact with one another, the decisions they make and how they behave.
Cost to Hire: The total cost to attract and recruit new employees. It can cover advertising, agencies, consultants, onboarding costs, equipment and relocation costs.
Crowd-sourcing: Sourcing goods or services from a large group of people, usually via the internet, which can include providing their feedback, opinions and thoughts. Sometimes these people are paid whilst others do it voluntarily. An example of this is the app – Waze. It allows users to report traffic jams and automatically give directions for other routes to take.
D
Desk-drop: To put items on employees’ desks that have a clear purpose and message to get across. This could be simply to say “thank you” or it could be rebrand launch.
Discretionary Effort: The effort an employee will put in over and above the expectations of their contract of employment and role. Think of it like “going the extra mile”.
E
Employee Engagement: The emotional commitment an employee has with an organisation and its goals. It can be influenced by the culture, leaders and an employee engagement programme. When employees feel engaged, performance improves and productivity increases.
Employee Experience: Each interaction an employee has with the business, from recruitment to onboarding to leaving the business.
Employee Relationship Management (ERM): The process of managing a relationship with the employee. A strong ERM programme helps ensure that employees are central to overall performance, both financial and operational, through effective regular collaboration.
Employee Survey: An employee survey is exactly that- a survey to employees. For example, this could be based on engagement or satisfaction. Using a third party to help create and conduct the survey, as well as analyse the results, helps employees’ confidence and participation levels.
Employee Turnover: The percentage of employees who leave an organisation over a set period (often on a yearly basis) and are more often replaced by new employees. Measuring specific segments of turnover data can be helpful when learning and understanding the reasons for this turnover.
Employee Value Proposition (EVP): EVP is what a company promises an employee to attract and retain them. It defines what an employee can expect from an employer and vice-versa. It aligns culture, mission and values, rewards, roles, purpose and people.
Employee Voice: This is when employees share their opinions and thoughts. The leadership team should listen carefully to these opinions as they can help shape the future of the business.
Exit Survey: Used for businesses to understand why an employee is leaving. From this feedback they can make improvements for future employees.
F
Face-to-face: When conversations take place in person as opposed to over the phone or via platforms such as Microsoft Teams. They are more personal and generally much more effective, as all senses involved in communication are experienced such as body language and eye contact.
Feedback: This is when employees share their thoughts and comments on a given subject. Continuous feedback will help the business to stay on the ball and make improvements.
Focus Group: A group of people who are asked to give honest opinions on a subject or product. Sometimes it’s better to have an employee moderate the session, rather than a leader, as dominant personalities can sway or influence opinions.
Formal Recognition: When recognition is given within a programme that has clear objectives and the employees are aware of the desired behaviours they must adopt in order to receive a reward.
G
Gifts: An item or experience given to an employee, usually for a job well done or a celebration. There has been a large amount of fear and uncertainty that sales incentives could fall foul of the bribery act and that companies operating such activities may be prosecuted for it. Read more about the bribery act here.
Gift Cards: A small card which can be exchanged for a cash value of gifts, usually from a specific retailer. However, you can buy gift cards which are redeemable cross multiple retailers e.g. Love2Shop. Gift cards can be physical plastic cards or digital whereby they have a unique gift code number.
H
HR: Stands for Human Resources and includes roles and functions that involve operational and strategic elements of people in a business. HR includes recruitment, engagement and training, to name but a few things.
I
Internal Communication (IC): Communication inside an organisation between a company and its audiences, which can include employees, contractors, shareholders, suppliers, stakeholders, unions, the community, potential employees and more. It includes both informal and formal communication.
Incentives: Something that encourages or motivates someone to do something or behave a certain way such as hitting a sales target. The incentive could be monetary or a non-monetary and part of an incentive programme (see below.)
Incentive Programme / Scheme: A programme where performance is rewarded with payments of cash, gifts, entitlements or experiences. Incentive programmes have defined performance levels and are often branded with associated communication and recognition strategies.
Induction: The process for introducing new employees to their role and organisation. It includes sharing company values, policies and procedures, as well as going through responsibilities and expectations.
Informal Recognition: Recognition of an employee’s contribution outside of any formal recognition programme. It is often spontaneous and delivered on the spot, at team meetings or via internal communications such as email.
Internal Communications Plan: How and what the business shares with the internal team. A structured plan will enable the business to share its objectives and the relevant tactics to achieve them. Check out this nine-step plan to help you get started.
Intranet: An internal website that employees can access to find company-related information, as well as other support such as benefits. It can also act as an engagement platform to share thoughts, ideas and comments.
L
Learning and Development: Where programmes are put in place to help an individual grow and enhance their skills and knowledge, usually aligned with the organisations vision, values and goals.
Long Service Awards: Employee recognition to honour those who have worked in the industry or company for a certain amount of time. It’s an opportunity for employers and managers to genuinely celebrate the contribution and hard work and employee has made in their time with the business.
M
Managers’ Discretionary Reward: A manager can provide ad-hoc reward and recognition either inside or outside of an official reward programme. It is often a way of rewarding informal recognition, while allowing managers to effectively reinforce values and behaviours.
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs: Maslow’s hierarchy is a motivational theory in psychology which includes a five tier model of human needs. His model, often illustrated as a hierarchical pyramid with the most fundamental needs at the bottom divides into basic or deficiency needs and growth needs – self-actualisation. The basic needs are said to motivate people if unmet, and motivate stronger the longer they are unmet. These needs have to be met in order to be able to progress, and are:
- Physiological – food, water, shelter, sleep, warmth, etc;
- Safety – security, law, order, freedom from fear;
- Social – friendship, love, affection and intimacy;
- Esteem – achievement, independence, status, prestige, self-respect, dominance, respect from others;
- Self-actualisation – self-fulfilment and realising potential, personal growth and peak experiences.
Morale: The confidence, spirit and enthusiasm from a group or person.
Motivation: A person’s level of effort and determination to want to be successful. People are motivated differently, therefore motivating employees can be a challenge as it’s unique to each individual. For example, some people are motivated to do a good job by having recognition from their manager, whereas others are motivated by a reward.
N
Nomination: The act of nominating or being nominated through an employee engagement programme. Employees can recognise their colleagues for going above and beyond.
O
Onboarding: The process of bringing employees into an organisation and preparing them for their role. It includes sharing knowledge they may need to help feel part of the company and become as productive as possible as quickly as possible. It can also involve formal training.
P
PDP: Personal Development Plan (PDP) is where employees map out what they want from their career and how they can get there. It includes development and training opportunities that will help enhance their skills and enable progression. Employers will sometimes use PDPs as part of their appraisal process, which is known as a Performance Development Review (PDR).
Peer-to-peer Communication: When information is shared ‘between ‘equals’ in an organisation.
Peer-to-peer Recognition: When an employee recognises another employee in an organisation for their hard work, efforts, teamwork, etc.
Perks: A term used informally to refer to something extra, or an advantage, you get as part of your employment. Can be items such as a car, phone, laptop, or other aspects like location or facilities, hence ‘perks of the job’. From perquisites, and historically used to describe executive benefits and entitlements.
Performance Review: When a manager evaluates and reviews job performance with their team, normally on a one-to-one basis. Performance reviews usually happen on a quarterly or annual basis. Less formal reviews may take place at more frequent intervals.
Productivity: How efficiently an employee is producing output. Increasing productivity could include better tools, more efficient processes, or increasing employee motivation.
Presenteeism: The practice of being present within the workplace but not fully functioning because of an illness, injury or other condition. Although they’re physically at work, they may have low productivity levels and not able to fully perform their duties, therefore more likely to make a mistake.
R
Recognition: Acknowledging an employee’s outstanding performance. Can be given formally by a manager via a recognition programme or informally by other colleagues.
Recognition Programme: Also known as a recognition scheme, they recognise and reward desired behaviours and performance of employees that support the organisations goals, values and culture. Recognition programmes are proven to improve employee engagement as individuals are rewarded and motivated to go the extra mile.
Recruitment: The process of attracting and employing new employee and fulfilling roles. Companies may choose to manage the recruitment of staff directly in-house or by using a number of external providers including outsourced staffing or recruitment agencies.
Remuneration: Compensation for time/effort of an employee, paid by the employer as money (wages, salary, bonuses), benefits and allowances.
Retention: The ability of a company to retain its employees. Employee retention is critical to achieving long-term successful, profitable and stable businesses. Recruiting and hiring is expensive and much knowledge is lost with talented employees leaving a business. New starters take time to resource, on board and get up to speed.
Reward: Giving an employee something in recognition of their services, efforts or achievements.
Reward Programme: When a company gives out rewards to their staff to encourage a particular behaviour and motivate them to perform well. – See recognition programme.
ROI: Stands for return on investment. A phrase given to the ‘proof’ that something is worth putting time, money and effort into as you’ll get more back than you put in.
S
Salary: A payment by an employer to an employee for an agreed role at an agreed rate, usually paid on a monthly basis but expressed as an annual amount.
Salary Sacrifice: An agreement to reduce an employee’s entitlement to cash pay, usually in return for a non-cash benefit.
SLT or SMT: Senior Leadership Team or Senior Management Team. Consists of the directors and most senior employees of a company.
Stand-up Meeting: A brief daily or weekly get together, typically 10 or 15 minutes. Great for focus and short-term information.
Stakeholders: The people who have an interest or influence in a business. This could be customers, the community, shareholders etc. From a marketing point of view, stakeholders are audiences to be considered and communicated with.
Strategy: A plan of action designed to achieve an overall aim. It includes setting the objectives and what tactics will help achieve them. An employee engagement strategy focuses on the actions taken to encourage employees to be more productive, engaged and establish an emotional connection with the business.
T
Talent Acquisition: The process of acquiring employees with specific skills to meet a specific organisational need. It is different to recruitment as it focuses on filling particular skills rather than a role.
Talent Retention: Where a business retains and develops employees with specific talents. Retention is a key strategic goal for many organisations with highly skilled employees given the costs of attraction and recruitment.
Tone of Voice: The way in which a business communicates its personality. Tone of voice is part of the brand identity and includes consistencies in communication, words and vocabulary used and the way in which the message is conveyed.
Top-down Communication: When company information flows from the higher levels of an organisation, typically the senior leadership team, through to the rest of the team. Also referred to as hierarchical communication.
Total Reward: Bringing together all the investments a business makes in its employees such as learning and development opportunities and/or an attractive working environment, in addition to the wider pay and benefits package.
Total Reward Statement: An annual statement produced for the employee and employer to document the total benefits the employee received and any liabilities due on parties each side.
U
User Generated Content: When employees share content for the business to use. It’s a great way to make the employee voice heard and encourage collaboration and engagement. This could be a guest blog or a testimonial on the website.
V
Values: A set of beliefs and principles upon which a business is based and drives the culture.
Vision: The aspiration of the future of a business. It includes where you want the business and gives the business a clear focus and direction to head in.